Inventory graph
Fix Security scrapes resources from your cloud providers. This data is the source of truth for all of Fix Security's features. All resources from all cloud providers, accounts, regions and all resource types become nodes in the graph.
Fix Security also knows how resources relate to each other. For example, a compute instance might have a volume and is attached to a network interface. The same compute instance might be the target of a load balancer, which is inside a security group, which itself is inside a VPC. All of these relationships are encoded as edges in the graph.
The superpower of Fix Security is the ability to provide a complete picture of your cloud assets and how they relate to each other.
Graph nodes
Each collected resource is a node in the asset inventory graph.
Resource data is encoded as a JSON document with a well-defined structure.
You can expect the following properties on every resource:
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
id | string | The cloud providers unique ID of a resource. This identifier might not be unique over different cloud providers. |
kind | string | The kind of the resource. See Resource Kinds below for details. |
name | string | The name of the resource. Fix Security tries its best to map the relevant property for that matter. |
ctime | datetime | The time the resource has been created. |
mtime | datetime | The time the resource has been modified the last time. |
atime | datetime | The time the resource has been accessed the last time. |
Resources have additional properties in addition to those above. The structure of the JSON document is defined by the resource kind.
Resource kinds
There is a plethora of resource types. Fix Security captures all of this information and makes it available to you.
To ensure you get consistent data, Fix Security defines a set of resource kinds. Each resource type is mapped to one of these kinds. Fix Security ensures that the data you get for a specific kind adheres to the schema defined for that kind.
The kind of resource is defined in the kind property of the resource.
Resource Models lists all available resource kinds.
The same resource can adhere to multiple resource kinds. This makes it possible to allow to view the same resource in more than one way. For example, an AWS EC2 volume can be viewed as aws_ec2_volume, as compute volume, as aws_resource and as resource.
This is useful if you want to search the graph using more abstract concepts. For example, it allows for the selection of all volumes regardless of cloud provider.
Graph edges
Fix Security also captures the relationships between resources by encoding the relationships as edges in the graph. This makes it possible to traverse the graph and walk from one resource to another based on a specific relationship. The relationship itself does not have any additional properties.
The list of possible edges are defined explicitly in Resource models.
This documentation describes how a resource might be connected. This does not mean that every relationship has to exist. For example, a compute instance might not have a volume attached to it. In this case, there is no edge between the compute instance and the volume.
Graph traversal
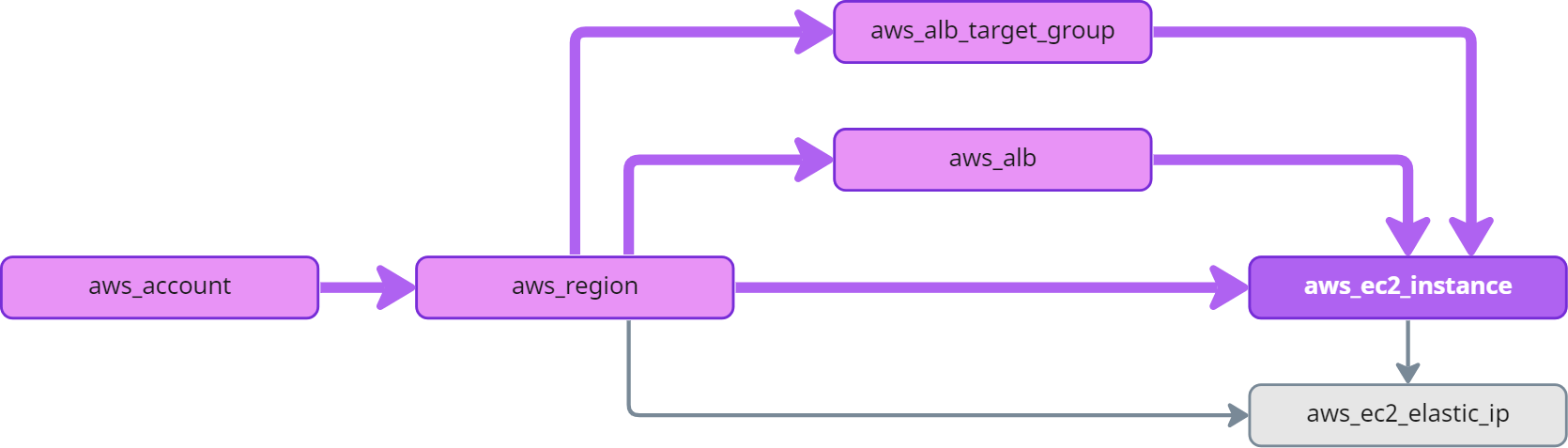
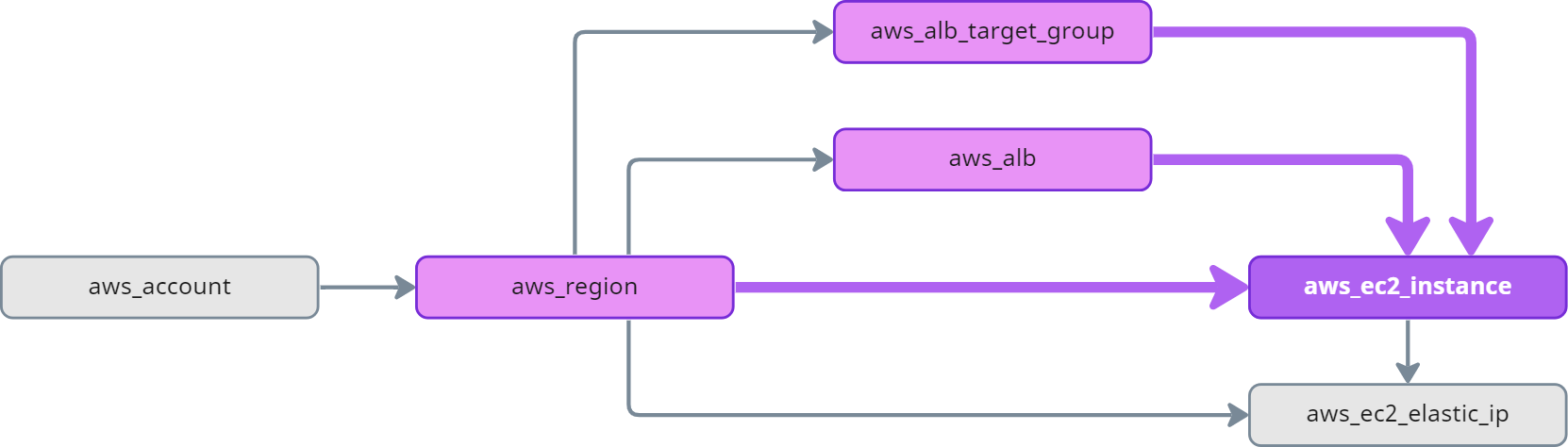
In order to traverse the graph in a meaningful way, it is important to understand the structure. The following diagram serves as an example graph you will find in Fix Security to illustrates how we can "walk" edges in a graph:
All resources in AWS are placed in a region. The region is a node in the graph. If we want to find all resources in the graph, we need to walk outbound (following the edges in direction of the arrow). If we want to know the account of a specific resource, we need to walk inbound (following the edge in reverse direction of the arrow) in the graph until we find an account.
Successors
Successor nodes are directly connected to the current node in an outbound direction.
aws_ec2_instance is a successor of aws_alb:
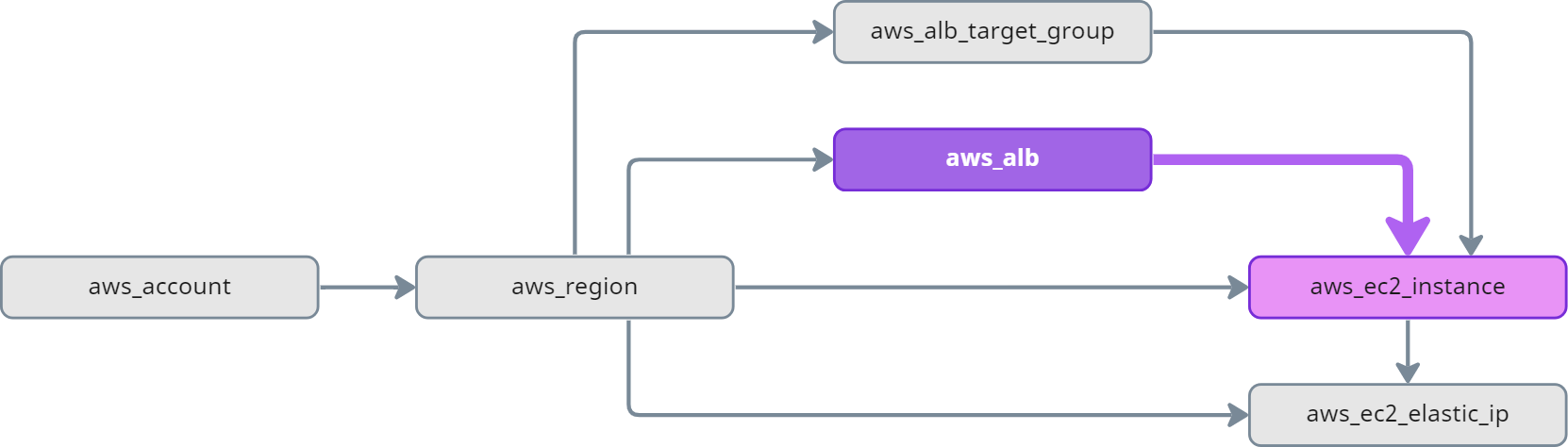
Descendants
Descendant nodes are directly or indirectly connected to the current node in an outbound direction (at any depth).
aws_ec2_instance and aws_ec2_elastic_ip are ancestors of aws_alb:
Predecessors
Predecessor nodes are directly connected to the current node in an inbound direction.
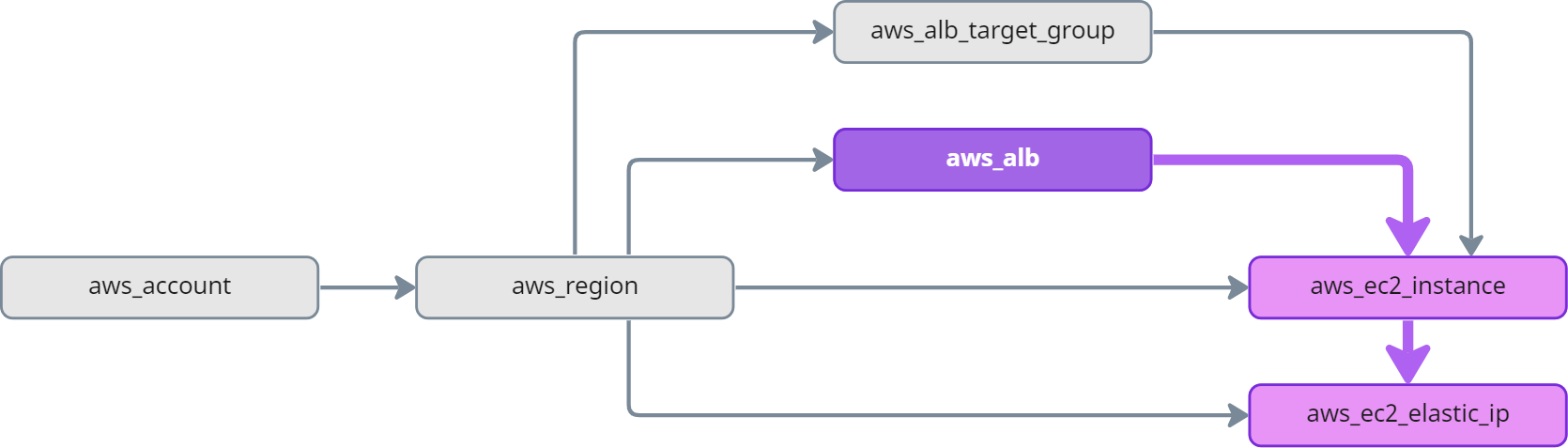
aws_region, aws_alb, and aws_alb_target_group are predecessors of aws_ec2_instance:
Ancestors
Ancestor nodes are directly or indirectly connected to the current node in an inbound direction (at any depth).
aws_region, aws_alb, aws_alb_target_group, and aws_account are ancestors of aws_ec2_instance: